Running Cypress Tests in Docker (Part 9)

こんにちは Kon'nichiwa,
This article series have been using Cypress v5.2.0; in this installment we will be using Cypress v9.2.0 (Why? I'll explain later)
There are multiple ways of how we can leverage Docker with a Cypress setup, in this article I'm mostly focused on how to integrate it best with the framework we have been building, so not entirely without prejudice.
Why Docker?
if you are an absolute beginner in terms of Docker, I would suggest you take a look at this nice article on InfoWorld.

To highlight a few points:
- Docker enables more efficient use of system resources
- You create your image once and run it anywhere on your local, inside ci/cd, or any other setups
- With Cypress, you can use Docker in your Continuous Testing setups achieving better results
So before we start you can also take a look at this brief article to get some know-how of how it works.

In the beginning
First, you can clone this repo here and run the following command in the terminal opened in your folder path
$ npm installthis should install all the required node dependencies.
we're not going to create a docker file for this project from scratch rather use cypress-docker-images if you want to explore that take a look at this article
There are three different types of cypress-docker-images and we'll be using cypress/included for one simple reason - it has it all!
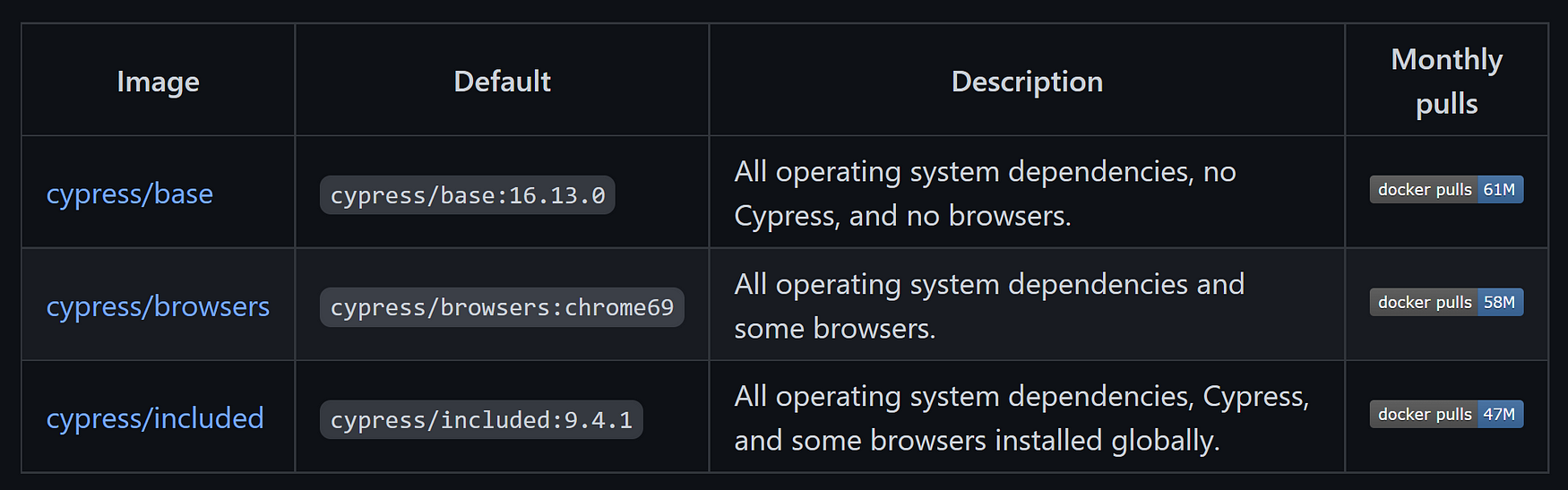
Assuming you already have Docker installed on your machine, let’s dive into running already built image cypress/included:9.2.0 which is also the sole reason we first upgraded our project to Cypress v9.2.0
In the terminal opened in your project location
$ docker run -it -v $PWD:/e2e -w /e2e cypress/included:9.2.0or if you are running windows like me then this command is slightly changed t0:
$ docker run -it -v ${PWD}:/e2e -w /e2e cypress/included:9.2.0This command is broken down into the following arguments

this command will run everything by getting the test specs details from cypress.json file and the result is as below:
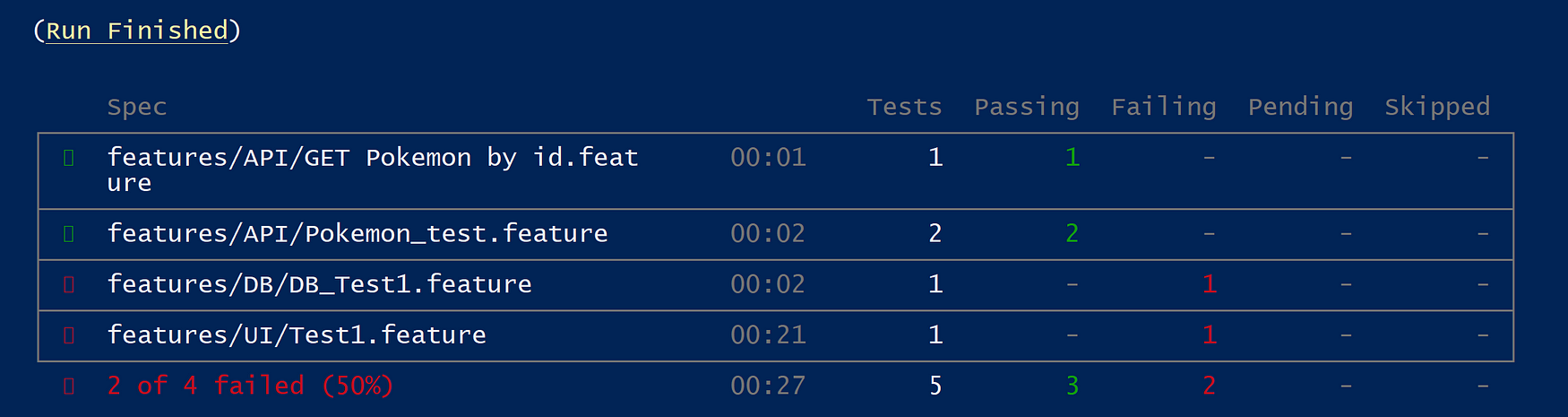
A bit explanation of what just happened:
cypress/included:9.2.0 has entry point set to ["cypress", "run"] which is equivalent of running npx cypress run on your local machine
which in our case is not that useful as everything is driven using runner.js which internally calls Cypress Module API.
Keep the container (Running from within the container)
Every time you run docker run you spawn a new container. That container then stops after the tests finish, but there is nothing Cypress can do about it - it is the Docker command docker run ... that controls this behavior.
If you are running a lot of tests, again and again, you might start the container once using Bash as the entry point, instead of the default cypress command. Then you can execute the cypress run or any other commands, while still in the same container:
In the terminal opened in your project location
PS D:\My____\Workspace\Cypress-TestFramework\Part 09> docker run -it -v ${PWD}:/e2e -w /e2e --entrypoint=/bin/bash cypress/included:9.2.0
root@BE4400671ae7:/e2e#further checking the content of the directory, it is the same as the one on your local machine
root@BE4400671ae7:/e2e# ls
cypress cypress.json node_modules package-lock.json package.json reports runner.jsnow you can go ahead and run the following command inside the docker, which is nothing but a script alias for command "node runner.js cypress run --env TAGS="@API" configFile=qa"
root@c239a1b9c99b:/e2e# npm run cy:test:qa
As you can see using our custom script we only ran the tests tagged with @API.
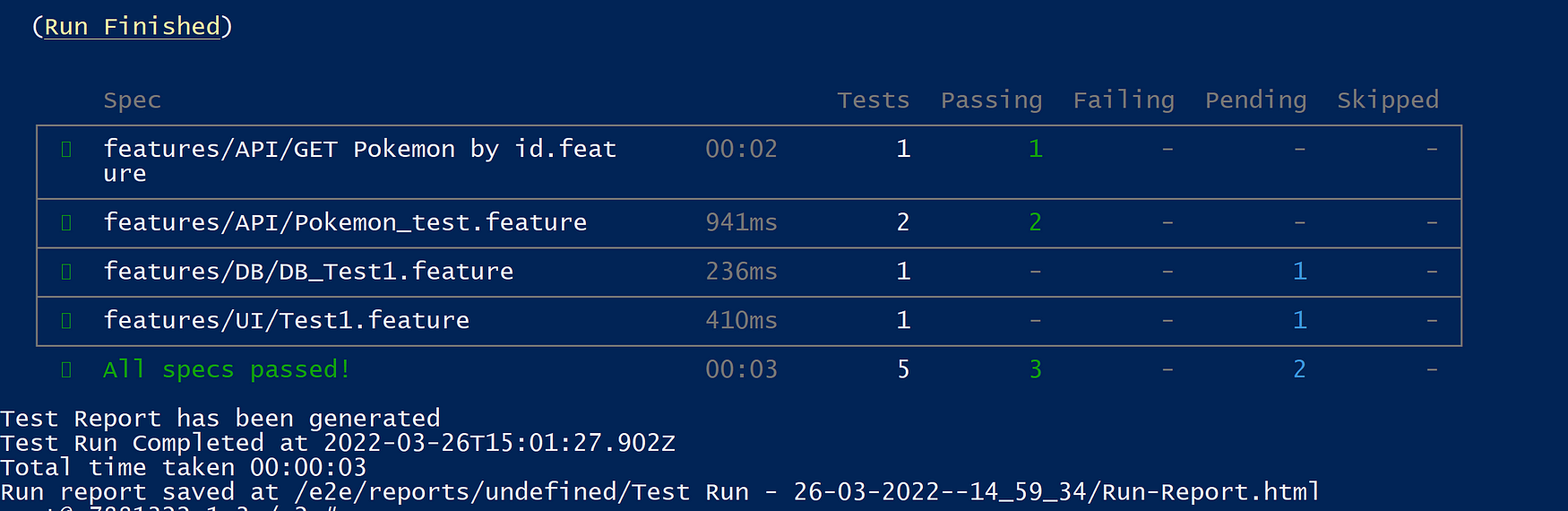
Once all the tests are finished results will be stored inside the originally mapped /e2e folder

Closing Notes:
In this article, we solely saw how we might run our Cypress Tests from the Cypress-TestFramework within a Docker container. How we actually leverage this in the ci/cd we will dive into that in an upcoming article "Running Cypress Tests in Github Actions (Part 10)".
Lest the reader complain; I didn't cover many different aspects of Docker such as building custom images and pushing them into Docker registry such as DockerHub, I might take a dig at that in the future. (Edit: you can read this article for more info )
さよなら Sayonara
Useful links:

Github Code:
https://github.com/far11ven/Cypress-TestFramework/tree/develop/Part 09







![Sanitizing ArrayBuffer response [shorts]](https://digitalpress.fra1.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/omtmgjm/2024/07/Screenshot-2024-07-02-145822-3.png)
![Cypress GitHub Teams Notification [shorts]](https://digitalpress.fra1.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/omtmgjm/2023/09/44036562.png)
![ChatGPT x Cypress.io API tests [shorts]](https://digitalpress.fra1.cdn.digitaloceanspaces.com/omtmgjm/2023/02/cypress-chatgpt.png)